One of our favorite features of PgAdmin is the graphical explain plan feature. While a graphical explain plan is not a complete
substitute for EXPLAIN or EXPLAIN ANALYZE text plans, it does provide a quick and easy to read view that can be used for further analysis.
In this article, we'll walk thru using
the explain plan to troubleshoot query performance.
To use the graphical explain plan feature in PgAdmin III - do the following
- Launch PgAdmin III and select a database.
- Click the SQL icon

- Type in a query or set of queries, and highlight the text of the query you want to analyse.
- Click the F7 button or go under Query->Explain or click the Explain Query icon
 .
.
- If you see no graphical explain plan, make sure that Query->Explain options->Verbose is unchecked - otherwise graphical explain will not work
- In terms of Explain option under the Query->Explain options-> you can choose Analyze which will give you the actual Explain plan in use and actual time and will take longer to run. Unchecking
this feature gives you the approximate explain plan and does not include time since its approximate. In terms of the graphical display - the raw display doesn't look too different between the 2, but if you click
on a section of the graph, a little tip will pop up showing the stats for that part of the graph. For analyze, you will see time metrics in the tip.
Here we look at the graphical explain plan of the two below queries querying against the demo pagila database.
Note that with constraint_exclusion off, both these
two queries have similar plans as shown in diagram below.
SELECT * FROM payment;
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT * FROM payment;
Result (cost=0.00..327.09 rows=18709 width=31) (actual time=0.010..20.240 rows=16049 loops=1)
-> Append (cost=0.00..327.09 rows=18709 width=31) (actual time=0.007..11.057 rows=16049 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on payment (cost=0.00..23.30 rows=1330 width=31) (actual time=0.001..0.001 rows=0 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_01 payment (cost=0.00..20.57 rows=1157 width=28) (actual time=0.006..0.340 rows=1157 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_02 payment (cost=0.00..40.12 rows=2312 width=28) (actual time=0.003..0.635 rows=2312 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_03 payment (cost=0.00..98.44 rows=5644 width=28) (actual time=0.003..1.521 rows=5644 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_04 payment (cost=0.00..117.54 rows=6754 width=28) (actual time=0.003..1.805 rows=6754 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_05 payment (cost=0.00..3.82 rows=182 width=27) (actual time=0.003..0.051 rows=182 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_06 payment (cost=0.00..23.30 rows=1330 width=31) (actual time=0.000..0.000 rows=0 loops=1)
Total runtime: 23.754 ms
AND
SET constraint_exclusion = 'off';
SELECT * FROM payment
WHERE payment_date BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-02-15';
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT * FROM payment
WHERE payment_date
BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-02-15';
Result (cost=0.00..420.63 rows=54 width=31) (actual time=0.262..5.193 rows=37 loops=1)
-> Append (cost=0.00..420.63 rows=54 width=31) (actual time=0.261..5.173 rows=37 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on payment (cost=0.00..29.95 rows=7 width=31) (actual time=0.001..0.001 rows=0 loops=1)
Filter: ((payment_date >= '2007-02-01 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)
AND (payment_date <= '2007-02-15 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone))
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_01 payment (cost=0.00..26.36 rows=1 width=28) (actual time=0.244..0.244 rows=0 loops=1)
Filter: ((payment_date >= '2007-02-01 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)
AND (payment_date <= '2007-02-15 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone))
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_02 payment (cost=0.00..51.68 rows=36 width=28) (actual time=0.014..0.598 rows=37 loops=1)
Filter: ((payment_date >= '2007-02-01 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)
AND (payment_date <= '2007-02-15 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone))
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_03 payment (cost=0.00..126.66 rows=1 width=28) (actual time=1.461..1.461 rows=0 loops=1)
Filter: ((payment_date >= '2007-02-01 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)
AND (payment_date <= '2007-02-15 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone))
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_04 payment (cost=0.00..151.31 rows=1 width=28) (actual time=2.683..2.683 rows=0 loops=1)
Filter: ((payment_date >= '2007-02-01 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)
AND (payment_date <= '2007-02-15 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone))
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_05 payment (cost=0.00..4.73 rows=1 width=27) (actual time=0.052..0.052 rows=0 loops=1)
Filter: ((payment_date >= '2007-02-01 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)
AND (payment_date <= '2007-02-15 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone))
-> Seq Scan on payment_p2007_06 payment (cost=0.00..29.95 rows=7 width=31) (actual time=0.000..0.000 rows=0 loops=1)
Filter: ((payment_date >= '2007-02-01 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)
AND (payment_date <= '2007-02-15 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone))
Total runtime: 5.287 ms

Now if we turn constraint_exclusion on - which, by the way you can make a global setting, in your PostgreSQL installation by modifying postgresql.conf
or via PgAdmin->Tools->Server Configuration->postgresql.conf. If you make a global setting, make sure to restart your PostgreSQL service/daemon or reload the config.
SET constraint_exclusion = 'on';
SELECT * FROM payment
WHERE payment_date
BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-02-15';
The graphical explain plan is displayed as shown below.
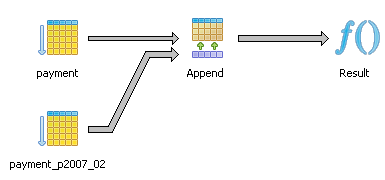
Note with constraint exclusion, the planner is analyzing the constraints in each of the tables and taking advantage of the fact that there is a constaint
on each of the inherited tables of the form
ALTER TABLE payment_p2007_03
ADD CONSTRAINT payment_p2007_03_payment_date_check
CHECK (payment_date >= '2007-03-01' AND payment_date < '2007-04-01');
and similar constraints on the other inherited payment tables to exclude them from queries where they should never have results.
As said earlier, to look into the details of timings etc, we can click on a section of the graphical explain plan
as shown here or just look at the raw explain plan text.
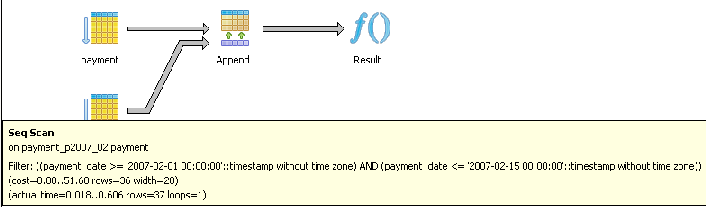
From the above we observe that with constrain exclusion on, our query has fewer tables to inspect. Constraint Exclusion is turned off by default in PostgreSQL config, so if you use partitioned tables, make sure to enable it in your postgresql.conf file. We also learn that
our query is doing a sequential scan of the data instead of an index scan. What if we added an index on the payment_date field, like so
CREATE INDEX idx_payment_p2007_02_payment_date
ON payment_p2007_02
USING btree(payment_date);
VACUUM ANALYZE;
and then rerun the same query
SELECT * FROM payment
WHERE payment_date
BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-02-15';
We see our query plan looks like this which is a bit different from before and is now using an indexed scan:
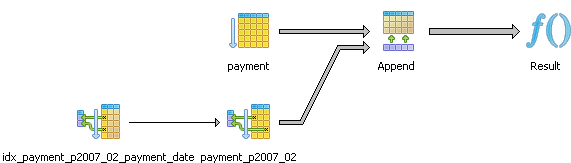
Below are some more interesting examples. Note: for our particular configuration, we can see that the planner has decided not to
utilize the customer_id index.
SELECT c.first_name, c.last_name, sum(p.amount) as total
FROM customer c INNER JOIN payment p ON c.customer_id = p.customer_id
WHERE payment_date BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-03-15'
GROUP BY c.first_name, c.last_name;
However if we force sequential scan off - it does
SET enable_seqscan = 'off';
SELECT c.first_name, c.last_name, sum(p.amount) as total
FROM customer c INNER JOIN payment p ON c.customer_id = p.customer_id
WHERE payment_date BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-03-15'
GROUP BY c.first_name, c.last_name;
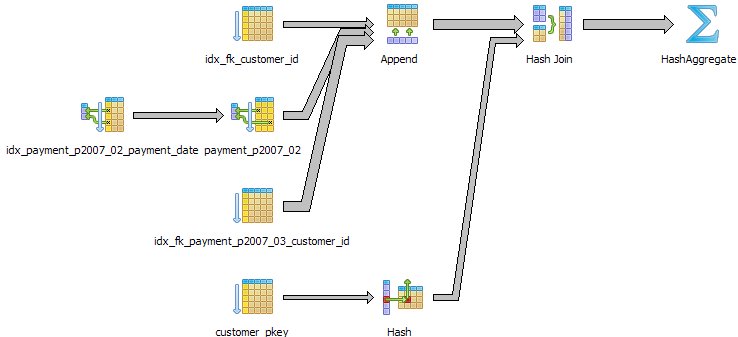
One may ask, that if the planner is capable of using 2 indexes simultaneously with bitmap heap index scans, why did it not
do so in this case without forcing its hand? If we compare the timings between the two approaches, they turn out to be pretty much the
same. Was the planner wrong not to use the customer index? Probably not. The reason is that even though we
have an index in place for customer_id on both tables, the fact that the customer list and number of customers purchasing items is
so small, doing a sequential table scan may be more efficient than using the index. Keep in mind that the planner
thinks like an economist, it sees the index as a resource and a resource that takes energy to consume. Consuming that resource
may be more costly than ignoring it. This is important to keep in mind for cases where you have small tables that don't expect
to increase or fields such as boolean fields. It is often wasteful to put indexes on these since they will rarely be used since a table
scan is more effective and indexes have cost in terms of needing to be updated during insert/update and having the planner even have to consider them. The planner uses table statistics to determine if an index is worthwhile to use. It is important that after large inserts/updates of data, one does a
VACUUM ANALYZE
to update statistics.
In this case, over time, the number of customers will increase so while the planner determines it is not useful to use now, increase in
data may change its mind.
There is another interesting thing about the graphical explain plan which is hard to see in these fairly simple examples.
There is meaning to the thickness of lines in the plan. A thicker line means more costly than a thinner line.
The graphical explain diagram also has a plethora of cute icons to display the various strategies in use which makes
it easy to spot problematic areas - especially for fairly large plans. Below is a query that
pulls the last sale for period February 2007 to March 15th 2007 for each customer who ordered during that period and sorts the
customers by last name and first name.
SELECT cp.*
FROM (SELECT DISTINCT ON (c.customer_id)
c.first_name, c.last_name , p.amount, p.payment_date
FROM customer c INNER JOIN payment p ON c.customer_id = p.customer_id
WHERE payment_date BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-03-15'
ORDER BY c.customer_id, p.payment_date DESC) As cp
ORDER BY cp.last_name, cp.first_name;
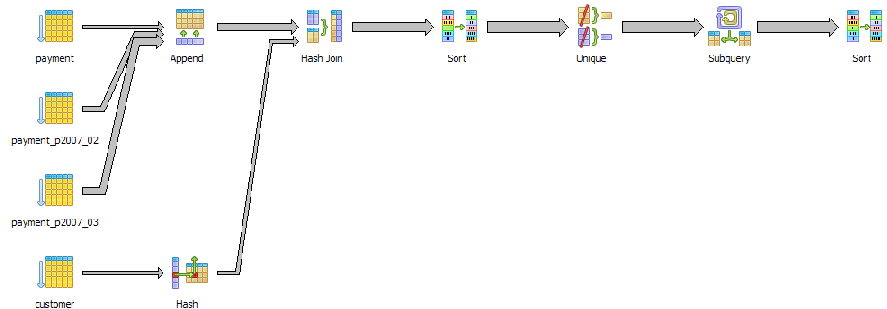
Here is another example that compares 2 different ways of selecting customers who did not purchase anything
between the '2007-02-01' and '2007-03-15'.
SELECT c.customer_id, c.last_name, c.first_name
FROM customer c LEFT JOIN
(SELECT customer_id
FROM payment p
WHERE p.payment_date BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-03-15') cp
ON c.customer_id = cp.customer_id
WHERE cp.customer_id IS NULL;
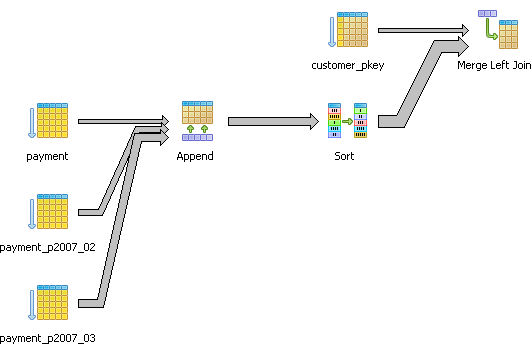 vs
vs
SELECT c.customer_id, c.last_name, c.first_name
FROM customer c
EXCEPT
SELECT c.customer_id, c.last_name, c.first_name
FROM payment p
INNER JOIN customer c ON p.customer_id = c.customer_id
WHERE p.payment_date BETWEEN '2007-02-01' and '2007-03-15';

Folgender Blog beschreibt sehr schön das explain-Statement von Postgres mit Hilfe des Admin-Tools pgadmin PGAdmin graphical Explain
Tracked: Feb 09, 12:26
What is Constraint Exclusion? Constraint Exclusion is a feature introduced in PostgreSQL 8.1 which is used in conjunction with Table Inheritance to implement table partitioning strategies. The basic idea is you put check constraints on tables to limit
Tracked: Mar 28, 15:57
The age old question of why or why is my table index not being used is probably the most common question that ever gets asked even by expert database users. In this brief article we will cover the most common reasons and try to order by statistical si
Tracked: Oct 28, 20:54
Tracked: Nov 05, 12:40
Tracked: Jul 12, 22:27
Tracked: Jan 16, 06:05